Barcan formula
In quantified modal logic, the Barcan formula and the converse Barcan formula (more accurately, schemata rather than formulae) (i) syntactically state principles or interchange between quantifiers and modalities; (ii) semantically state a relation between domains of possible worlds. The formulae were introduced as axioms by Ruth Barcan Marcus, in the first extensions of modal propositional logic to include quantification. [1]
Related formulas include the Buridan formula, and the converse Buridan formula.
Contents |
The Barcan formula
The Barcan formula is:
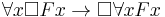 .
.
In English, the schema reads: If everything is necessarily F, then it is necessary that everything is F. It is equivalent to
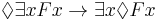 .
.
The Barcan formula has generated some controversy because it implies that all objects which exist in every possible world (accessible to the actual world) exist in the actual world, i.e. that domains cannot grow when one moves to accessible worlds. This thesis is sometimes known as actualism--i.e. that there are no merely possible individuals. There is some debate as to the informal interpretation of the Barcan formula and its converse.
Converse Barcan formula
The converse Barcan formula is:
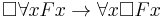 .
.
If a frame is based on a symmetric accessibility relation, then the Barcan formula will be valid in the frame if, and only if, the converse Barcan formula is valid in the frame. It states that domains cannot shrink as one moves to accessible worlds, i.e. that individuals cannot cease to be possible. The converse Barcan formula is taken to be more plausible than the Barcan formula.
References
- ^ Journal of Symbolic Logic (1946),11 and (1947), 12 under Ruth C. Barcan
External links
- Barcan both ways by Melvin Fitting
- Contingent Objects and the Barcan Formula by Hayaki Reina